SnowflakeIDGenerator 1.5.2024.337
dotnet add package SnowflakeIDGenerator --version 1.5.2024.337
NuGet\Install-Package SnowflakeIDGenerator -Version 1.5.2024.337
<PackageReference Include="SnowflakeIDGenerator" Version="1.5.2024.337" />
paket add SnowflakeIDGenerator --version 1.5.2024.337
#r "nuget: SnowflakeIDGenerator, 1.5.2024.337"
// Install SnowflakeIDGenerator as a Cake Addin #addin nuget:?package=SnowflakeIDGenerator&version=1.5.2024.337 // Install SnowflakeIDGenerator as a Cake Tool #tool nuget:?package=SnowflakeIDGenerator&version=1.5.2024.337
Snowflake Id Generator
Generate unique identifiers based on Twitter's Snowflake ID. Parse a Snowflake to get information about it's creation.
| More info | API |
|---|
Snowflakes
Snowflakes (or SnoflakeIds) are a form of generating identifiers used in distributed computing that, when used properly, guarantees uniqueness between systems, since one of it's components refers to the system creating the ID.
The other components refer to the current date and time, in order not to keep track of a long running sequencer (for example, a sequence in a database), and a short (in memory) sequence, to allow the generation of several codes in a short amount of time.
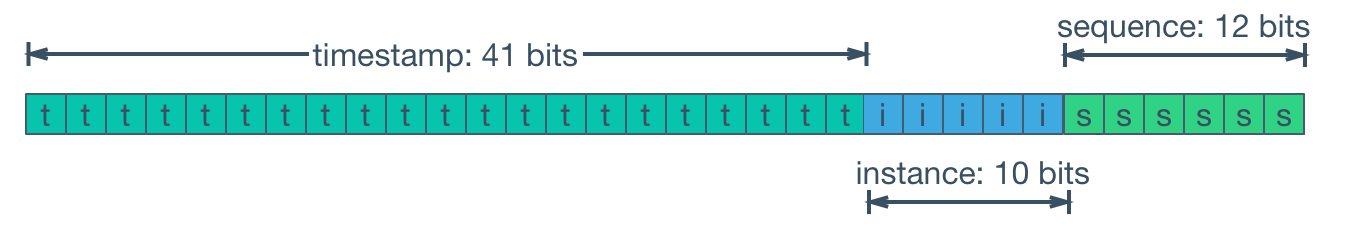 |
|---|
| Image Source & credit available in wikimedia. "instance" in this image replaces machineId in the library / package |
Usage
Generate
There are 2 ways of using the generator:
- Using the
SnowflakeIDGeneratorclass as a static class. Useful when generating a single code to avoid dealing with constructors and the scope of the generator object. - Instantiating the
SnowflakeIDGeneratorclass. Recommended if you plan to generate more than a few codes at the same time.On version 1.4.2024 and up you can use the interface
ISnowflakeIDGenerator. If you prefer to use dependency injection, the package SnowflakeIDGenerator.DependencyInjection might be helpful.
Using the SnowflakeIDGenerator class
- Instantiate class
SnowflakeIDGenerator
SnowflakeIDGenerator generator = new SnowflakeIDGenerator(machineId);
where machineId is the number / identifier of the system currently trying to get an id
Starting on version 1.1.2023 you can instruct the generator to use a custom date as epoch from which the timestamps are derived for the current date.
SnowflakeIDGenerator generator = new SnowflakeIDGenerator(machineId, CustomEpoch);
- Using the generator object, there are 3 ways of obtaining the code:
- Call
generator.GetSnowflake()to get aSnowflakeobject - Call
generator.GetCode()to get an Id in number (ulong) format - Call
generator.GetCodeString()to get an Id in string format
- Call
Using the SnowflakeIDGenerator class as static
If you only need to get a single Id, it's easier to just use the generator class as static.
The method names are the same as when using the generator, except they need the machineId as parameter:
- Call
SnowflakeIDGenerator.GetSnowflake(machineId)to get aSnowflakeobject - Call
SnowflakeIDGenerator.GetCode(machineId)to get an Id in number (ulong) format - Call
SnowflakeIDGenerator.GetCodeString(machineId)to get an Id in string format
Using a non-standard date as epoch
version 1.1.2023 and up
The first component of the codes is the amount of milliseconds elapsed since a set point in time, called epoch. By default, the generator uses the unix epoch (jan-1-1970 12:00:00am) as starting point to count.
Adding a DateTime object as an extra parameter when using the generator allows to change the zero value to be used to count milliseconds to.
DateTime customEpoch = new DateTime(year: 2020, month: 1, day: 1, hour: 0, minute: 0, second: 0, DateTimeKind.Utc);
// Creating the generator class
SnowflakeIDGenerator generator = new SnowflakeIDGenerator(machineId, customEpoch);
// This works when using as static too!
SnowflakeIDGenerator.GetSnowflake(machineId, customEpoch)
Parsing an Id
Parse a Snowflake either from a string or a number (ulong) in order to get information regarding the generation, such as the time or the machine that generated the code.
If a custom epoch was used when generating, that DateTime must be passed as second parameter when parsing in order to get the right generation date.
string s = "06975580616378931208";
ulong n = 6975580821430984519ul;
Snowflake fromString = Snowflake.Parse(s);
var utcDateTimeFromString = fromString.UtcDateTime; // 13/9/2022 22:26:58
var timestampFromString = fromString.Timestamp; // 1663108018965
var machineIdFromString = fromString.MachineId; // 477
var sequenceFromString = fromString.Sequence; // 2056
Snowflake fromNumber = Snowflake.Parse(n);
var utcDateTimeFromNumber = fromNumber.UtcDateTime; // 13/9/2022 22:27:47
var timestampFromNumber = fromNumber.Timestamp; // 1663108067853
var machineIdFromNumber = fromNumber.MachineId; // 701
var sequenceFromNumber = fromNumber.Sequence; // 3911
Additionally, starting on version 1.2.2023 you can cast a string or a number (ulong) directly into a Snowflake
without using the Parse() method (only when using the default epoch).
string s = "06975580616378931208";
ulong n = 6975580821430984519ul;
Snowflake fromString = (Snowflake)s;
var utcDateTimeFromString = fromString.UtcDateTime; // 13/9/2022 22:26:58
var timestampFromString = fromString.Timestamp; // 1663108018965
var machineIdFromString = fromString.MachineId; // 477
var sequenceFromString = fromString.Sequence; // 2056
Snowflake fromNumber = (Snowflake)n;
var utcDateTimeFromNumber = fromNumber.UtcDateTime; // 13/9/2022 22:27:47
var timestampFromNumber = fromNumber.Timestamp; // 1663108067853
var machineIdFromNumber = fromNumber.MachineId; // 701
var sequenceFromNumber = fromNumber.Sequence; // 3911
The Snowflake object
While the SnowflakeIDGenerator class keeps track of time, machine and sequence,
a Snowflake object keeps track of the meaning of the code, and allows to extract information about said code.
For example, as seen on the parsing an Id section, when working with a Snowflake object
(either parsed or just generated), you can see some information. The available fields are:
UtcDateTime: The creation date (UTC format)TimestampandTimestampInt64The timestamp component of the code. Amount of milliseconds since the configured epochMachineIdandMachineIdInt32: the machine / terminal / server that created the idSequenceandSequenceInt32: The sequencer. If greater than 0, multiple ids where generated withing the same millisecondId: The Snowflake id inulongformatCode: The Snowflake id asString
Changing Epoch on generated codes
If you need to change the epoch on an already generated code,
use ChangeEpoch() to change it keeping the same code but changing the represented date,
or use RebaseEpoch() to keep the date but changing the final code.
| Product | Versions Compatible and additional computed target framework versions. |
|---|---|
| .NET | net5.0 was computed. net5.0-windows was computed. net6.0 is compatible. net6.0-android was computed. net6.0-ios was computed. net6.0-maccatalyst was computed. net6.0-macos was computed. net6.0-tvos was computed. net6.0-windows was computed. net7.0 was computed. net7.0-android was computed. net7.0-ios was computed. net7.0-maccatalyst was computed. net7.0-macos was computed. net7.0-tvos was computed. net7.0-windows was computed. net8.0 is compatible. net8.0-android was computed. net8.0-browser was computed. net8.0-ios was computed. net8.0-maccatalyst was computed. net8.0-macos was computed. net8.0-tvos was computed. net8.0-windows was computed. net9.0 is compatible. |
| .NET Core | netcoreapp1.0 was computed. netcoreapp1.1 was computed. netcoreapp2.0 was computed. netcoreapp2.1 was computed. netcoreapp2.2 was computed. netcoreapp3.0 was computed. netcoreapp3.1 was computed. |
| .NET Standard | netstandard1.3 is compatible. netstandard1.4 was computed. netstandard1.5 was computed. netstandard1.6 was computed. netstandard2.0 is compatible. netstandard2.1 is compatible. |
| .NET Framework | net20 is compatible. net35 is compatible. net40 is compatible. net403 was computed. net45 was computed. net451 was computed. net452 was computed. net46 was computed. net461 was computed. net462 was computed. net463 was computed. net47 was computed. net471 was computed. net472 was computed. net48 was computed. net481 was computed. |
| MonoAndroid | monoandroid was computed. |
| MonoMac | monomac was computed. |
| MonoTouch | monotouch was computed. |
| Tizen | tizen30 was computed. tizen40 was computed. tizen60 was computed. |
| Universal Windows Platform | uap was computed. uap10.0 was computed. |
| Xamarin.iOS | xamarinios was computed. |
| Xamarin.Mac | xamarinmac was computed. |
| Xamarin.TVOS | xamarintvos was computed. |
| Xamarin.WatchOS | xamarinwatchos was computed. |
-
.NETFramework 2.0
- No dependencies.
-
.NETFramework 3.5
- No dependencies.
-
.NETFramework 4.0
- No dependencies.
-
.NETStandard 1.3
- NETStandard.Library (>= 1.6.1)
- System.Threading.Thread (>= 4.3.0)
-
.NETStandard 2.0
- No dependencies.
-
.NETStandard 2.1
- No dependencies.
-
net6.0
- No dependencies.
-
net8.0
- No dependencies.
-
net9.0
- No dependencies.
NuGet packages (1)
Showing the top 1 NuGet packages that depend on SnowflakeIDGenerator:
| Package | Downloads |
|---|---|
|
SnowflakeIDGenerator.DependencyInjection
Extends package SnowflakeIDGenerator to help in configuring the snowflakeId generator using dependency injection |
GitHub repositories
This package is not used by any popular GitHub repositories.
| Version | Downloads | Last updated | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5.2024.337 | 163 | 12/2/2024 | |
| 1.5.2024.306 | 3,537 | 11/1/2024 | |
| 1.4.2024.131 | 2,650 | 5/10/2024 | |
| 1.3.2023.287 | 336 | 10/14/2023 | |
| 1.2.2023.201 | 994 | 7/20/2023 | |
| 1.1.2023.147 | 184 | 5/27/2023 | |
| 1.0.2023.145 | 163 | 5/25/2023 | |
| 1.0.2022.283 | 475 | 10/10/2022 | |
| 1.0.2022.268 | 506 | 9/25/2022 | |
| 1.0.2022.261 | 456 | 9/18/2022 | |
| 1.0.2022.257 | 467 | 9/14/2022 | |
| 1.0.2022.256 | 618 | 9/13/2022 |
# Changelog
## 1.5
- Slightly improved performance
- Improved documentation
## 1.4
- Added dependency injection helpers using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection.
- To avoid package dependency bloating, this was added to package SnowflakeIDGenerator.DependencyInjection
- Added class SnowflakeIdGeneratorOptions to Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection to help with automatic initialization from configuration.
## 1.3.2023
- Solved an issue that caused the custom epoch sometimes not being saved to the snowflake object. This does not affects the generated codes, but could make them to return the wrong date when parsed
- Comparisons should be between snowflakes using the same epoch
- Equality comparer returns false if the snowflakes being compared use different epochs
## 1.2.2023
- Added ability to change and rebase epoch to an already generated code
- Added implicit casting from Snowflake to string and ulong
- Added explicit casting to Snowflake from string and ulong
## 1.1.2023
- Added ability to use a custom epoch
## 1.0.2023
- Throw exception if time moves backwards
## 1.0.2022
- Initial version
